Next week it will come into force in Spain when it is verified that a positive no longer contaminates after that time of confinement
The Public Health Commission has approved the reduction of the quarantine period for close contacts from 14 to 10 days and the incorporation of antigenic tests as a diagnostic and screening tool.
These measures have been adopted within the framework of updating the “Strategy for the early detection, surveillance and control of COVID-19”, according to the Ministry of Health in a statement.
The Commission has decided, as anticipated by the Minister of Health, Salvador Illa, and the Generalitat of Catalonia had already approved, to reduce the quarantine of close contacts to 10 days (from the last contact with a confirmed case).
For mild cases, isolation is maintained for 10 days from the onset of symptoms, provided that at least 3 have elapsed without presenting any symptoms. If these circumstances arise, it will not be necessary to carry out a diagnostic test to lift said isolation or to return to work.
In asymptomatic cases that are positive, the isolation will be maintained for 10 days from the date of taking the sample for diagnosis. Follow-up will be supervised until epidemiological discharge in the manner established by each autonomous community.
Regarding the work environment, health and social health personnel that turns out to be a confirmed case and does not require hospital admission, will follow the same guidelines as the general population regarding isolation.
But these workers will have to undergo a diagnostic test that indicates that they have exceeded the period of transmissibility of the infection so that they can return to their job.
The new measures establish that depending on the epidemiological situation of each community, a diagnostic test may be recommended during the quarantine period.
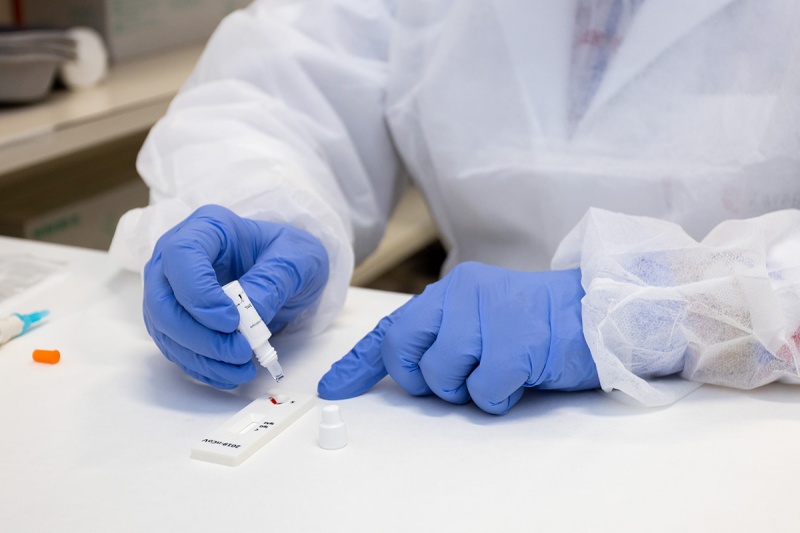
Health explains in its statement that there are currently two tests to detect covid infections: a rapid detection of antigens and a detection of viral RNA through PCR or an equivalent molecular technique.
“The update of the Strategy includes the use of both tests in the different scenarios of diagnosis and follow-up of cases and contacts,” according to Health, to “facilitate the diagnosis and that it can be carried out as quickly as possible.”
Thus, the appropriate control measures will be able to be implemented and it will be possible to face “the foreseeable increase in the coming months of the diagnostic needs due to the increase in respiratory infections such as influenza.